Question 4
Answer : (4) 5, 2, 517
Explanation Question 4
A union is a special data type available in C that allows to store different data types in the same memory location. You can define a union with many members, but only one member can contain a value at any given time. Unions provide an efficient way of using the same memory location for multiple-purpose.
4. What is the output of the following ‘C’ program ?
(Assuming little - endian representation of multi-byte data in which Least Significant Byte (LSB) is stored at the lowest memory address.)
(Assuming little - endian representation of multi-byte data in which Least Significant Byte (LSB) is stored at the lowest memory address.)
Answer : (4) 5, 2, 517
Explanation Question 4
A union is a special data type available in C that allows to store different data types in the same memory location. You can define a union with many members, but only one member can contain a value at any given time. Unions provide an efficient way of using the same memory location for multiple-purpose.
| Previous | Next |
| UGC-NET CS 2018 July - II Question 3 | UGC NET CS 2018 July - II Question 5 |
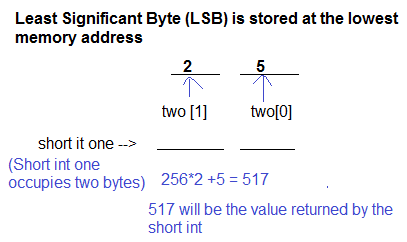

#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>
/* Assume short int occupies two bytes of storage */
int main ( )
{
union saving
{
short int one;
char two[2];
};
union saving m;
m.two [0] = 5;
m.two [1] = 2;
printf(’’%d, %d, %d\n”, m.two [0], m.two [1], m.one);
}/* end of main */